Life cycle of stars [ part 1 of 2 ]
Life cycle of stars ( PART 1 of 2)
What are stars ? How do they form ? What is evolution of stars ? How do they affect us and some other questions related to stars and their importance in universe will be sought out in this blog. 👇 👇 👇
What are stars ?
Stars are nothing but hot and dense spheres of gases in which the elements ignite / burn themselves for generating energy which keeps the star at constant temperature and brightness.
Forces in a star : There are mainly 2 forces acting in any star namely the gravitational force which pulls the particles towards the star and the pressure of the hot gasses in the star due to which the particles are thrown away from the star. While these 2 forces are constant the star remains stable.
Birth and evolution of stars : Stars are born out of large nebulas. These nebulas have large numbers of elements in them. Slowly with time the gravitational force in them increases due to which they contract and become hot and dense. At this state they start burning these elements as fuels for generating energy. Sometimes the nebulas are so large that thousands of stars are formed out of them . Based on their initial size , stars have 3 paths of evolution
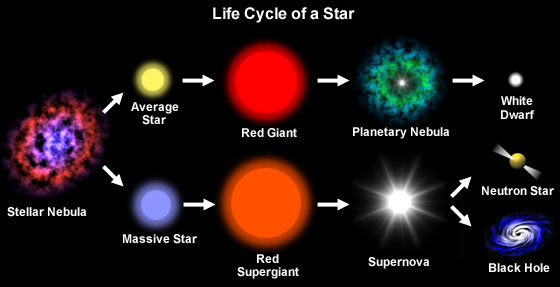
1st path of evolution : The stars which have an initial mass of less or similar to that of our sun ( < mass of sun ) undergo this path of evolution. At the beginning these stars are a low mass stars . But over time , hydrogen ( the basic element which stars ignite at their initial state ) in these stars gets less and the hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei. After hydrogen gets completely finished , these stars start to burn helium. In this process the star undergoes great changes and it expands over a large area . Such stars are called as red giants. They are called so because of their giant mass and particular red colour. Later again after billions of years helium starts to finish off and again they fuse together to form heavier elements. In this process again a huge explosion happens ( even bigger than the first one !!! ). This is known as a supernova explosion. Due to this explosion the outer cover of the stars atmosphere blows out and only the inner white core remains. In this stage the pressure of gasses remains constant ever after ignition completely stops and is capable of balancing the gravitational force forever. This is the end stage of stars and stars in this stage are known as white dwarfs.
The next 2 paths of the evolution will be discussed in the next blog. Do read it by clicking this link. Hope u all enjoyed reading and if yes then don't forget to like and share !!! 🙂🙂🙂
Comments